The main elements that make an assembly happen are Fasteners, support systems, Locks, Latches, Hinges, Handles, Knobs, Gaskets and Seals, Cable management systems in case of electronic equipment, and many such elements. Out of this, we had reviewed fasteners in the earlier chapter “Sheet Metal Joinery”. Let us briefly review the others in this chapter before looking into the methods of assembly.
Some of the accessories in assemblies are as follows:
1. Hinges
A hinge is a mechanical bearing that connects two parts and allows rotation relative to each other along a common fixed axis. In sheet metal technology hinges can be inbuilt or off-shelf hinges can be used.
Pin Hinges
 Pin hinge.
Pin hinge.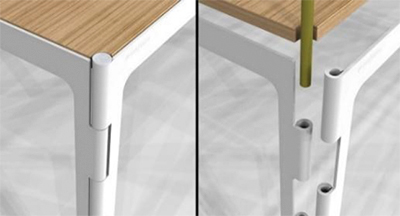 A pin hinge creative application in assembling the legs of a table. (Image source)
A pin hinge creative application in assembling the legs of a table. (Image source)Pin hinges are used when the second rotating part is not fixed rigidly to the hinge. Pin hinges enable easy insertion of one part into another.
But Hinge
A butt hinge has two rectangular leaves with knuckles in the middle, joined by a pin. It is the most common hinge used on doors, the standard choice for light doors. Ball-bearing butt hinges are more durable and last longer. Spring-loaded butt hinges (also called self-closing butt hinges) contain a spring that automatically closes a door.
Hinges with metallic inserts and Studs
Concealed Hinge
 Custom fabricated hinge.
Custom fabricated hinge.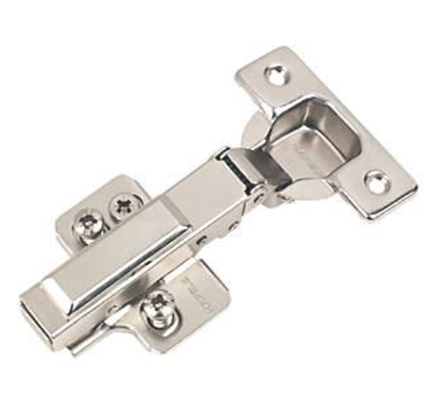 Standard concealed hinges. (Image source)
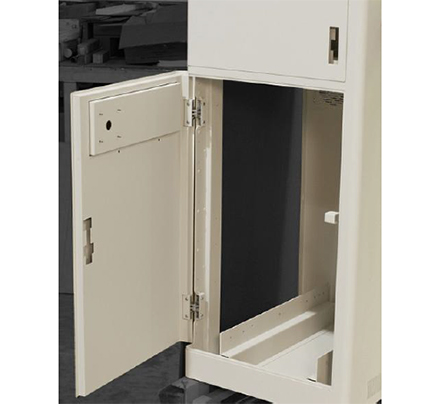
Standard concealed hinges. (Image source) A concealed hinge in assemby. (Image source)
A concealed hinge in assemby. (Image source)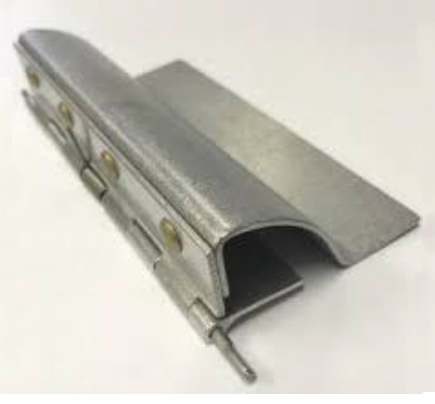 A concealed hinge in assemby. (Image source)
A concealed hinge in assemby. (Image source)Concealed hinges are used where they cannot be seen from outside. They provide a smooth, uninterrupted appearance that is aesthetically pleasing. Also, because they cannot be tampered with from the outside, they provide security.
Knife Hinge/Pivot Hinge
Hinges or pivot hinges may open fully or may have stops to restrict the movement. These are often used in doors to be fixed to a cabinet. Only the pivot point is visible after installation.
Panel Board hinges are very economical, used extensively in Panel Boards. Barrel hinges are useful when axial loads are less. They are fixed to the edge of the panel’s piano hinge, also known as a continuous hinge that tends to span the entire length of a door or a lid continuously. Piano hinges are easy to install, are very affordable, and are extremely durable. The disadvantage is the maintenance as they tend to easily accumulate dust and grime.
Spring Hinges
 Spring hinge.
Spring hinge.Spring hinges are self-closing hinges. A spring mechanism in the barrel allows the hinges to automatically close a door. A spring-loaded hinge makes it possible to lock the door in a fully open or fully closed position.
Things to consider in designing a hinge
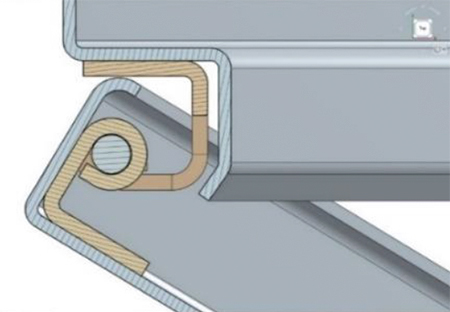
When designing a concealed hinge, the often-encountered problem is an interference of the panel with respect to hinge pin location. Much study and care are needed to avoid interference. It is a tight balance between pivot location versus panel thickness.
2. Latches / Locks
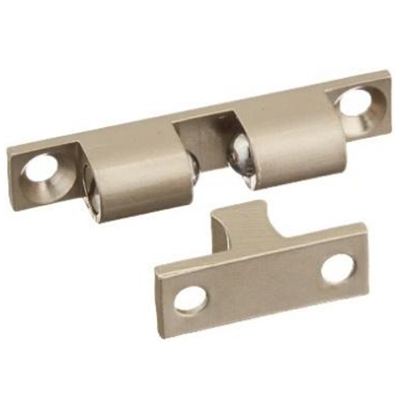
Ball and Roller Catches
Ball and roller catches are widely used in domestic shelving applications. They are durable and long-lasting . Most often these types of catches use non-ferrous materials to prevent rusting. The applied force required to detach a mating part depends upon the compressive force of the spring which applies pressure on the ball.
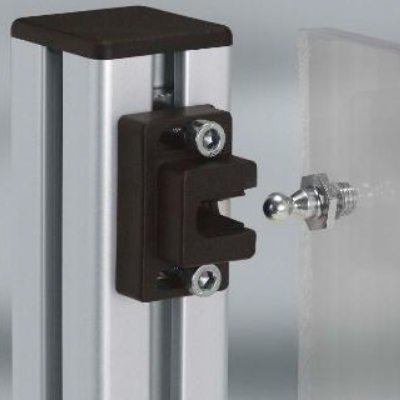
Magnetic Latch
One advantage of mag latch is that magnets as thin as the sheet itself are available for easy concealing and be flush with the sheet. Excessive contact pressure between the magnet and mating part is detrimental to the purpose. Effects of Jarring caused while applying excessive pull force are not good for the durability of parts besides being uncomfortable.
3. Slides
There are many varieties of slides available commercially. Heavy duty to light duty, self-locking, self-closing, push to open etc., Slides are widely used to access serviceable parts and sub-assemblies.
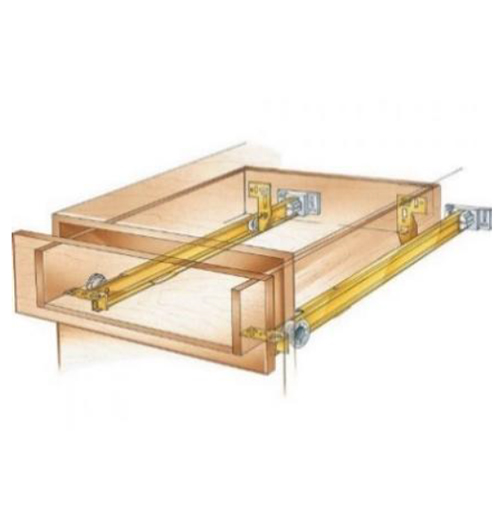 A 19” Sub Rack mounted on slides. Facilitates access to back panel wiring and Components.
A 19” Sub Rack mounted on slides. Facilitates access to back panel wiring and Components.(Image source)
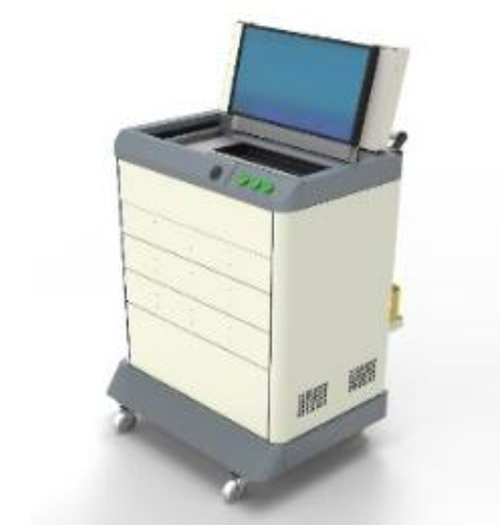 A Medical Cart uses “push to open” slides to open the drawers, eliminating protruding handles.
A Medical Cart uses “push to open” slides to open the drawers, eliminating protruding handles.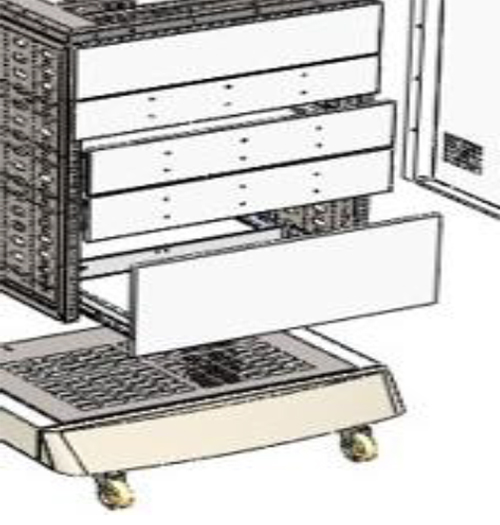 A Medical Cart uses “push to open” slides to open the drawers, eliminating protruding handles.
A Medical Cart uses “push to open” slides to open the drawers, eliminating protruding handles.Galling
 Galled Threads.
Galled Threads.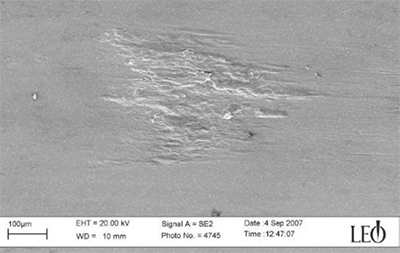 Galled sheet surface (Courtesy : leo)
Galled sheet surface (Courtesy : leo)
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces caused by friction. It tears into metal and causes slipping between two sliding surfaces. Galling commonly happens between two metal surfaces that are in sliding contact with each other. It is especially common where there is inadequate lubrication between the surfaces. Aluminium galls very easily, whereas hardened steel resistant to galling. Some of the ways to prevent galling are to use slides or incorporate embossed dimples between the sliding parts.



 (
( Panel Board Hinges.
Panel Board Hinges. Panel Board Hinges.
Panel Board Hinges. Panel Board Hinges.
Panel Board Hinges. Barrel Hinge.
Barrel Hinge. Piano hinge.
Piano hinge. Spring loaded hinge.
Spring loaded hinge.



 (
( (
( (
( Heavy duty slides.
Heavy duty slides. Undermount slides.
Undermount slides. Soft closing slides.
Soft closing slides.