Examples of 3D Metal Printing
Printing Process
Surface Finish
 Cracking.
Cracking.
(Image courtesy of Albert To and University of Pittsburgh’s Swanson School of Engineering.)
Warpage
Image courtesy of International Materials Reviews.
(Image source)
The cost of 3D printing is typically calculated as the cost of the powder used plus the machine time per hour. The machine time per hour price may vary from INR 2000 to 5000 depending upon the machine.
Few things to consider in 3D metal printing:
Wall Thickness - Maintain minimum wall thickness recommended by powder manufacturers.
Slits and gaps - Too narrow slits in the component tend to close.
Bridges - Inadequately supported bridges tend to collapse.
Hole Diameter - Maintain minimum hole diameters.
Overhangs - Cantilever projections, overhangs to have minimum recommended lengths.
1. Virtual Manufacturing
Excerpts from an article authored by Prof P P Date, Dept of Mech Engg, IIT-Bombay

 CAD Model and actual componenti
CAD Model and actual componenti
While 3D printing is not truly a part of sheet metal processes in the context of this book, it is not out of the way to learn something about this process as additive manufacturing which is known as 3D printing as it is bound to replace many conventional metalworking processes soon.
Metal 3D printing is considered the apex of all 3D printing. Metal 3D Printing is a laser-based technology that uses powdered metals. DMLS (direct metal laser sintering), SLM (selective laser melting), and EBM (electron beam melting) methods are commonly used methods of printing. Like Laser Sintering, a high-powered laser selectively binds together particles on the powder bed while the machine distributes even layers of metallic powder. Support structures are automatically generated and built simultaneously in the same material and are later manually removed. Once complete, the part undergoes heat treatment.
Printing Process
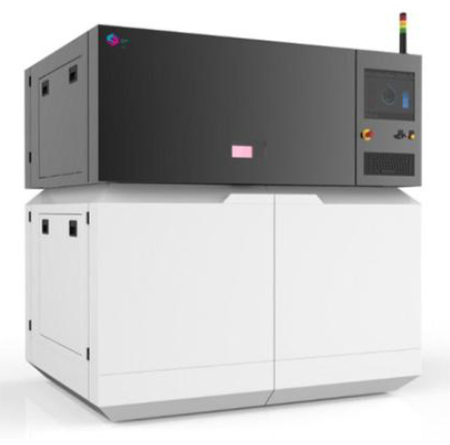

A 3D Metal Printing Machine (Image source)
Issues in 3D Metal Printing
3D printing however is not without its problems. Lot of preparatory work goes into the work. Much attention needs to be given to the CAD model to avoid possible problematic issues. Some of the problem areas are as follows:
Surface Finish

An example of surface finish before and after machining. (Image courtesy NASA)
Surface finish quality is most often rough and requires post-printing operations like machining. There is a trade-off involved between surface finish and cost.
Porosity

Courtesy: (3printr.com)
Porous cavities may occur due to certain gas formations or due to process anomalies during printing. It is important to control the quality of the powder, laser spot size, and intensity to avoid pores. Also, powder density and porosity are interrelated. A good printed part should at least have 90 % density.
Residual Stresses
 Cracking.
Cracking.
(Image courtesy of Albert To and University of Pittsburgh’s Swanson School of Engineering.)
Residual stresses may occur due to expansion and contraction as a result of heating and cooling of the part while printing. This may lead to defects such as warpage or cracking of the substrate material during the solidification process. The quantum of energy applied also plays a role.
Warpage

Image courtesy of the Center for Additive Manufacturing and Logistics at North Carolina State University.
(Image source)
Thermal stresses induced in support structures or varying thicknesses can cause warpage to the component. To prevent warpage, it’s necessary to place the ideal number of support structures in the right locations.
Delamination
Image courtesy of International Materials Reviews.
(Image source)
The cost of 3D printing is typically calculated as the cost of the powder used plus the machine time per hour. The machine time per hour price may vary from INR 2000 to 5000 depending upon the machine.
Few things to consider in 3D metal printing:
Wall Thickness - Maintain minimum wall thickness recommended by powder manufacturers.
Slits and gaps - Too narrow slits in the component tend to close.
Bridges - Inadequately supported bridges tend to collapse.
Hole Diameter - Maintain minimum hole diameters.
Overhangs - Cantilever projections, overhangs to have minimum recommended lengths.
1. Virtual Manufacturing
Excerpts from an article authored by Prof P P Date, Dept of Mech Engg, IIT-Bombay


Given the increasing complexity of part geometries, together with ever-expanding options from the availability of a spectrum of materials and processes, getting the part ‘first time right’ appears to be a difficult proposition, unless modern techniques of simulation are used. Simulation software has been continuously incorporating these advancements into their database to predict the strains and the potential locations of failure in the part being formed. Virtual manufacturing will take the centre stage soon, since one can get a feel for how close the formed part would be, to the geometry intended by the designer.
Virtual manufacturing of sheet metal parts will have to account for the variations introduced by the inevitable variations in material properties, tool wear, tool deflection under load, and some inconsistency in spring back. While different stakeholders are working on the consistency of the final product quality, each of the above-mentioned factors will continue to bring in an element of uncertainty since the interaction material variations with almost every major parameter (like product geometry, tool design and tool geometry, sheet thickness, etc) impacts the final characteristics of the sheet metal part. Unless variations in material properties are curtailed, generous tolerances will have to be assigned to the dimensions and the philosophy of functional build will have to be adopted.


 (
( (
( (
( CAD Model.
CAD Model. Laser impinging.
Laser impinging. Powder layer replinishment.
Powder layer replinishment. 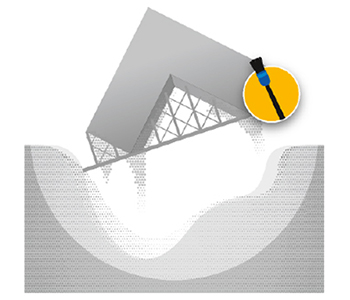 Power Removal.
Power Removal. Part Removal.
Part Removal. Heat Treatment.
Heat Treatment. Residual Stress defects.
Residual Stress defects.